Blockchain technology is often touted for its unparalleled ability to offer secure, transparent, and tamper-resistant systems for recording transactions and data. One of the foundational aspects that make blockchain so secure and trustworthy is its inherent immutability. Immutability refers to the property that once data has been written to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This characteristic plays a critical role in ensuring the integrity and security of the information stored on the network. In this article, we will explore how immutability enhances blockchain security and why it is a crucial feature for various industries adopting blockchain-based solutions.
How Immutability Ensures Data Integrity
Immutability is central to the concept of data integrity in blockchain systems. Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it is confirmed by multiple nodes across the network using consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). This decentralized validation process ensures that no single party can tamper with the data without the collective agreement of the network participants.
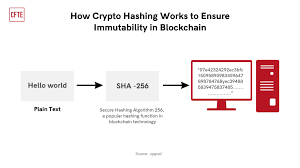
Each block in the blockchain contains a unique cryptographic hash of the previous block, which is used to link the blocks together in a secure chain. This hashing mechanism makes it nearly impossible to alter a block’s content once it has been added to the blockchain. Even a small change to the data would result in a completely different hash value, which would break the chain. This cryptographic linkage ensures that any attempt to modify a transaction would be immediately detected by other network participants, preventing fraudulent alterations.
The role of immutability extends beyond just preventing unauthorized changes; it also serves as a deterrent for malicious activity. The difficulty in altering the blockchain data without detection makes it highly secure, as any modification attempt would require immense computational resources and consensus approval from a majority of the network. This immutability provides a sense of trust, especially in industries where data accuracy is critical, such as finance, healthcare, and supply chain management.
Building Trust in Digital Transactions
Trust is a fundamental aspect of any digital transaction, and immutability plays a crucial role in establishing and maintaining this trust in blockchain systems. In traditional systems, trust is often placed in intermediaries, such as banks or notaries, who verify transactions and ensure their accuracy. However, this model can be vulnerable to manipulation, fraud, and errors. Blockchain removes the need for intermediaries by using decentralized consensus mechanisms and cryptographic techniques to guarantee the integrity of transactions.
For instance, in the financial sector, blockchain’s immutability ensures that once a transaction has been recorded, it cannot be reversed or altered. This is particularly important for preventing fraud or double-spending. Similarly, in the supply chain industry, blockchain allows for transparent and tamper-proof tracking of goods as they move through various stages. Since each transaction is immutable, participants can trust the recorded data, which fosters a more secure and efficient system for managing goods, verifying provenance, and ensuring authenticity.
Immutability also enhances accountability. In situations where disputes arise, such as contract fulfillment or legal agreements, the immutable nature of the blockchain can provide a verifiable record of actions taken. The transparent and unchangeable ledger allows all parties involved to trace back every decision or transaction, ensuring that accountability is preserved and reducing the likelihood of fraud or negligence.
Challenges and Considerations in Immutability
While immutability is a powerful feature of blockchain, it also brings certain challenges and considerations. One such challenge is the difficulty in correcting errors once they are recorded on the blockchain. If a mistake is made, such as an incorrect transaction, it cannot simply be erased or modified. This could pose a problem in use cases where flexibility or the ability to correct errors is necessary, such as in personal data management or systems where data may need to be updated frequently.
Moreover, immutability may raise privacy concerns, particularly in sectors that require sensitive personal data. While blockchain ensures data integrity, the public nature of some blockchain networks means that anyone can view the transaction history. This creates a potential conflict between the need for transparency and the requirement for privacy. Solutions such as zero-knowledge proofs and permissioned blockchains are being explored to address these privacy concerns while still maintaining immutability.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of immutability in ensuring security and trust far outweigh the limitations. The ability to provide a permanent, unalterable record of transactions creates a robust framework for secure and transparent systems, whether in financial services, supply chains, or other industries.
Why Immutability Matters for the Future of Blockchain
The role of immutability in blockchain security will continue to grow in importance as more industries adopt blockchain-based solutions. As businesses increasingly rely on blockchain for secure, transparent, and tamper-proof record-keeping, the need for immutability will be central to their trust in the system. Immutability not only protects against fraud and unauthorized changes but also helps build a more resilient and trustworthy digital economy.
As blockchain technology evolves, new techniques and enhancements will likely emerge to address its challenges while preserving the core principles of immutability and security. Innovations in private and permissioned blockchains, as well as advances in cryptographic methods, will ensure that immutability remains a fundamental feature that enhances the security and reliability of blockchain networks.
In conclusion, immutability is one of the most powerful and transformative features of blockchain technology. By providing a secure, tamper-proof environment for recording transactions and data, blockchain establishes trust, accountability, and transparency in a way that traditional systems cannot match. As more industries and sectors embrace blockchain, the role of immutability in ensuring security and data integrity will remain crucial for the continued success and adoption of blockchain-based solutions.